September 24th, 2024
The process of turning an initial design concept into a mass-produced plastic product is filled with challenges, uncertainties and potential pitfalls. With so many possible faults, it is vital to ensure the soundness of your design before commencing the actual production. This is where prototyping plays a central role within injection molding.
Prototyping is not merely a preliminary step; it is a critical phase that can significantly impact the success, proficiency and cost-effectiveness of the entire operation. Therefore, it’s essential to understand the benefits and how to best utilize this step.
What is Prototyping in Injection Molding?
Prototyping involves the creation of an early, working model of a part or product. This mock-up serves as a tangible precedent for the intended outcome and is used to test and compare various aspects of the design, including aesthetic appeal, performance and manufacturability. Designers and engineers are able to visualize the physicality of the final piece, identify potential flaws and make needed changes before committing to full-scale production. The process can be repetitive, often involving multiple rounds of simulation to fine-tune and optimize before proceeding to fabrication stage.
Why Prototyping is Crucial
Design Validation and Refinement
Prototyping presents a key opportunity to try out and tweak designs. By building a physical replica, developers can assess the form to physically see it in a real-world context. This hands-on evaluation helps in identifying defects or areas for refinement that may not be apparent in a digital mode. For example, issues related to symmetry, geometry, thickness or assembly are detected early on, then adjustments are made to correct where necessary.
Cost Efficiency
Producing an injection mold is quite costly, particularly when complex parts are desired. A single mistake or imperfection discovered after the piece has been created could translate to significant financial losses if a modification or complete alteration is needed. Prototyping mitigates such possibilities by ensuring that the design is fully vetted before the mold design is finalized. By catching and correcting errors during prototype testing/evaluation, manufacturers can avoid costly delays and revisions, which ultimately saves time and money.
Accelerated Time-to-Market
In today’s competitive market, speed is often a prominent factor in a product’s success. Prototyping helps to streamline the developmental aspect by enabling prompt refinements. With modern technologies such as 3D printing and CNC machining, samples can be produced quickly, leading to faster decision-making and any required changes. This agility promotes a shorter development cycle, facilitating manufacturers bringing their products to the market quicker.
Improved Communication and Collaboration
Prototypes serve as a powerful communication tool, bridging the gap between designers, engineers, stakeholders and clients. A physical copy gives all parties an opportunity to conceptualize the product, discuss its feasibility and provide feedback in a more concrete way than with digital renderings alone. This collaborative approach fosters a better comprehension of project goals, aligns expectations and ensures that everyone is on the same page, reducing the likelihood of misunderstandings or misaligned objectives.
Risk Mitigation
Manufacturing inherently involves risk, particularly when making complex parts with tight tolerances or new attributes. Prototyping helps to mitigate these perils by leaving room for thorough evaluation and validation before committing to full-scale manufacture. Businesses reduce defects, failures and other damaging fallout that could arise if potential problems are caught early in the development stage.
Prototyping Methods in Injection Molding
Several prototyping methods are commonly used in the plastic injection molding industry, each offering unique advantages depending on the specific requirements of the project. Some common techniques include:
3D Printing
3D printing is a popular way to generate low-cost prototypes fast. It allows for the rapid production of complicated geometries and involved framework that might be difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional manufacturing approaches. This medium is particularly useful for early-stage models where speed and flexibility are imperative.
CNC Machining
CNC machining entails the use of computer-controlled machines to form prototypes from solid blocks of material. This process is extremely precise and can make samples that closely resemble the final injection-molded part in terms of material properties and surface appearance. CNC machining is often applied to construct high-fidelity prototypes that require specific dimensional tolerances and material characteristics.
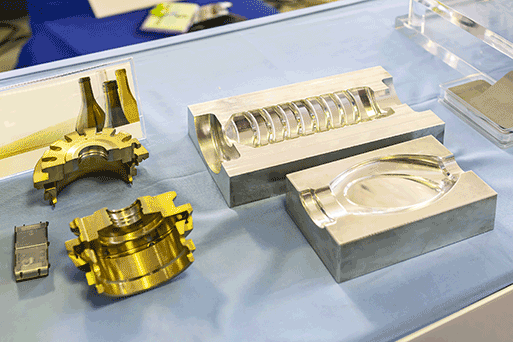
Soft Tooling
Soft tooling, also known as silicone molding, encompasses creating a prototype mold from silicone, which can then be utilized to produce a small number of parts. This is beneficial for making prototypes that must closely resemble the final injection-molded part in terms of material facets and manufacturing procedure. Soft tooling is a cost-efficient way to put out functional prototypes in limited quantities.
The Impact of Prototyping on the Final Product
The value of prototyping extends far beyond the first steps of the design and development period. A well-executed plan lays the foundation for a substantial production run, safeguarding that the outcome meets or exceeds expectations. By thoroughly analyzing and confirming design standards, substances and performance guidelines during this phase, manufacturers can achieve better quality, greater consistency and improved functionality in the final composition. Additionally, the insights gained from these paradigms can help advise future projects, leading to continuous advancement and innovation in the injection molding industry.
For these reasons and more, prototyping is an essential component in the plastic injection molding industry, providing manufacturers with the tools and insights needed to bring their products to life with confidence. From design confirmation and budgetary efficiency to accelerated time-to-market and risk mitigation, the paybacks of prototyping are clear and compelling. By investing in a robust prototyping course, businesses can be assured that their products not only meet the highest standards of quality and performance but also deliver value to their customers and stakeholders. In a competitive market where precision, capability and modernization are paramount, prototyping is not just important – it is indispensable.